| [1]许士凯. 现代抗衰老化学药物研究进展(之一) [J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2005,14(16):2083-2086.
[2]卞志高.从<内经>看中医学的抗衰老理论[J].四川中医,2003, 21(1):12-13.
[3]李昕,张洁,宋佳霖,等.传统灸疗法抗衰老研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(2):450-454.
[4]冯艺萍,葛为公.抗衰老药物的使用现状及研究进展[J].华夏医学,2006,19(2):360-363.
[5]朱志明.抗衰老药物应用的若干问题[J].实用老年医学,2002, 16(2): 73-75.
[6]许士凯.抗衰老药物源性毒副反应的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2005,14(22):2911-2912.
[7]Alexanian AR, Maiman DJ, Kurpad SN, et al.In vitro and in vivo characterization of neurally modified mesenchymal stem cells induced by epigenetic modifiers and neural stem cell environment.Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6):1123-1130.
[8]Deng X, Chen YX, Zhang X, et al.Hepatic stellate cells modulate the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells.J Cell Physiol. 2008; 217(1):138-144.
[9]Zhao D, Wu H, Li F,et al.Electromagnetic field change the expression of osteogenesis genes in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2008;28(2):152-155.
[10]Dezawa M.Systematic neuronal and muscle induction systems in bone marrow stromal cells: the potential for tissue reconstruction in neurodegenerative and muscle degenerative diseases.Med Mol Morphol. 2008;41(1):14-19.
[11]Tsuji W, Inamoto T, Yamashiro H,et al.Adipogenesis induced by human adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(1):83-93.
[12]Jung Y, Chung YI, Kim SH,et al.In situ chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells in a TGF-beta1 loaded fibrin-poly(lactide-caprolactone) nanoparticulate complex.Biomaterials. 2009;30(27):4657-4664.
[13]Saulnier N, Lattanzi W, Puglisi MA,et al.Mesenchymal stromal cells multipotency and plasticity: induction toward the hepatic lineage.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2009;13 Suppl 1:71-78.
[14]Marshall BL.The New Virility: Viagra, Male Aging and Sexual Function. Sexualities. 2006;9(3):345-362.
[15]Neves D, Santos J, Tomada N,et al.Aging and orchidectomy modulate expression of VEGF receptors (Flt-1 and Flk-1) on corpus cavernosum of the rat.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006; 1067: 164-172.
[16]Smith CP, Steinle JJ.Changes in Growth Factor Expression in Normal Aging of the Rat Retina. Exp Eye Res. 2007; 85(6): 817-824.
[17]Ponte AL, Marais E, Gallay N,et al.The in vitro migration capacity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: comparison of chemokine and growth factor chemotactic activities.Stem Cells. 2007;25(7):1737-1745.
[18]Chamberlain JR, Schwarze U, Wang PR,et al.Gene targeting in stem cells from individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta. Science. 2004;303(5661):1198-1201.
[19]Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(14):8407-8411.
[20]Rasulov MF, Vasilchenkov AV, Onishchenko NA,et al.First experience of the use bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of a patient with deep skin burns.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2005;139(1):141-144.
[21]李军,张洹,刘革修.移植胎鼠间充质干细胞的抗衰老作用[J].生理学报,2010, 62(1): 79-85.
[22]李旭,李宝平.骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠实验性肺气肿的作用[J].中国医药导报,2010,7(3):11-13.
[23]Brunet A, Rando TA.Ageing: from stem to stern.Nature. 2007; 449(7160):288-291.
[24]王英杰,徐阿炳,董萍,等.衰老分子机理的各种学说[J].中国老年学杂志,1994,14(4): 246-249.
[25]欧芹,翟饶生,王玉民,等.棉花根对老年小鼠红细胞和脑内SOD活性及MDA含量的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,1994,14(2):106-107.
[26]Cheng J, Türkel N, Hemati N,et al.Centrosome misorientation reduces stem cell division during ageing. Nature. 2008; 456 (7222):599-604.
[27]Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience.J Intern Med. 2007;262(5): 509-525.
[28]朱亚珍,朱虹光.D-半乳糖致衰老动物模型的建立及其检测方法[J].复旦学报:医学版,2007,34(4):617-619.
[29]曹湘博,于乐洋,常雅萍. D-半乳糖亚急性中毒拟衰老模型鼠免疫功能及生化指标变化的研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2007, 17(7): 382-385.
[30]Conboy IM, Conboy MJ, Wagers AJ,et al.Rejuvenation of aged progenitor cells by exposure to a young systemic environment. Nature. 2005;433(7027):760-764.
[31]Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N,et al. Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):661-669.
[32]Zhou K, Zhang H, Jin O,et al.Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell ameliorates the autoimmune pathogenesis in MRL/lpr mice.Cell Mol Immunol. 2008;5(6): 417-424.
[33]李宝平,赵晓建,宋永明,等.血管生成因子修复肺气肿病变的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2007,87(33):2365-2368.
[34]Tang K, Rossiter HB, Wagner PD,et al.Lung-targeted VEGF inactivation leads to an emphysema phenotype in mice.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004;97(4):1559-1566. |
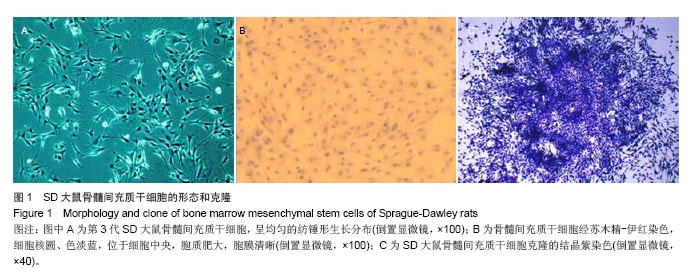
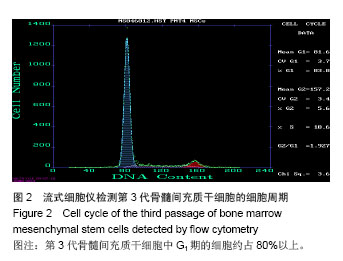
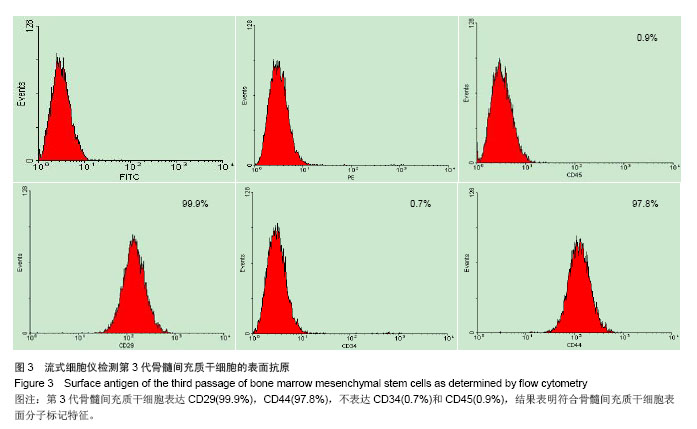
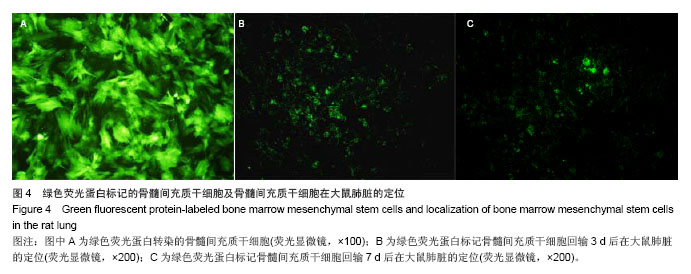
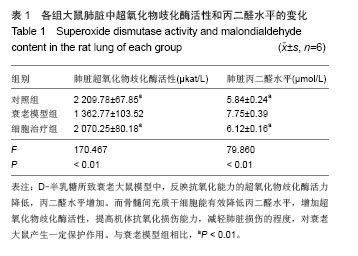
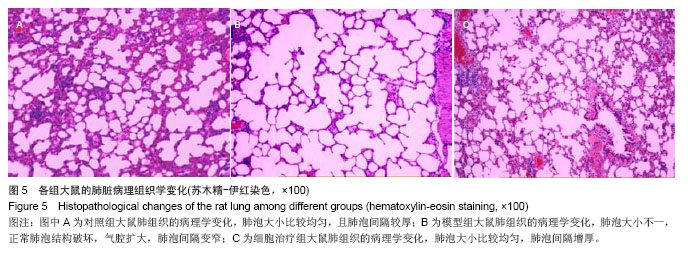
.jpg)